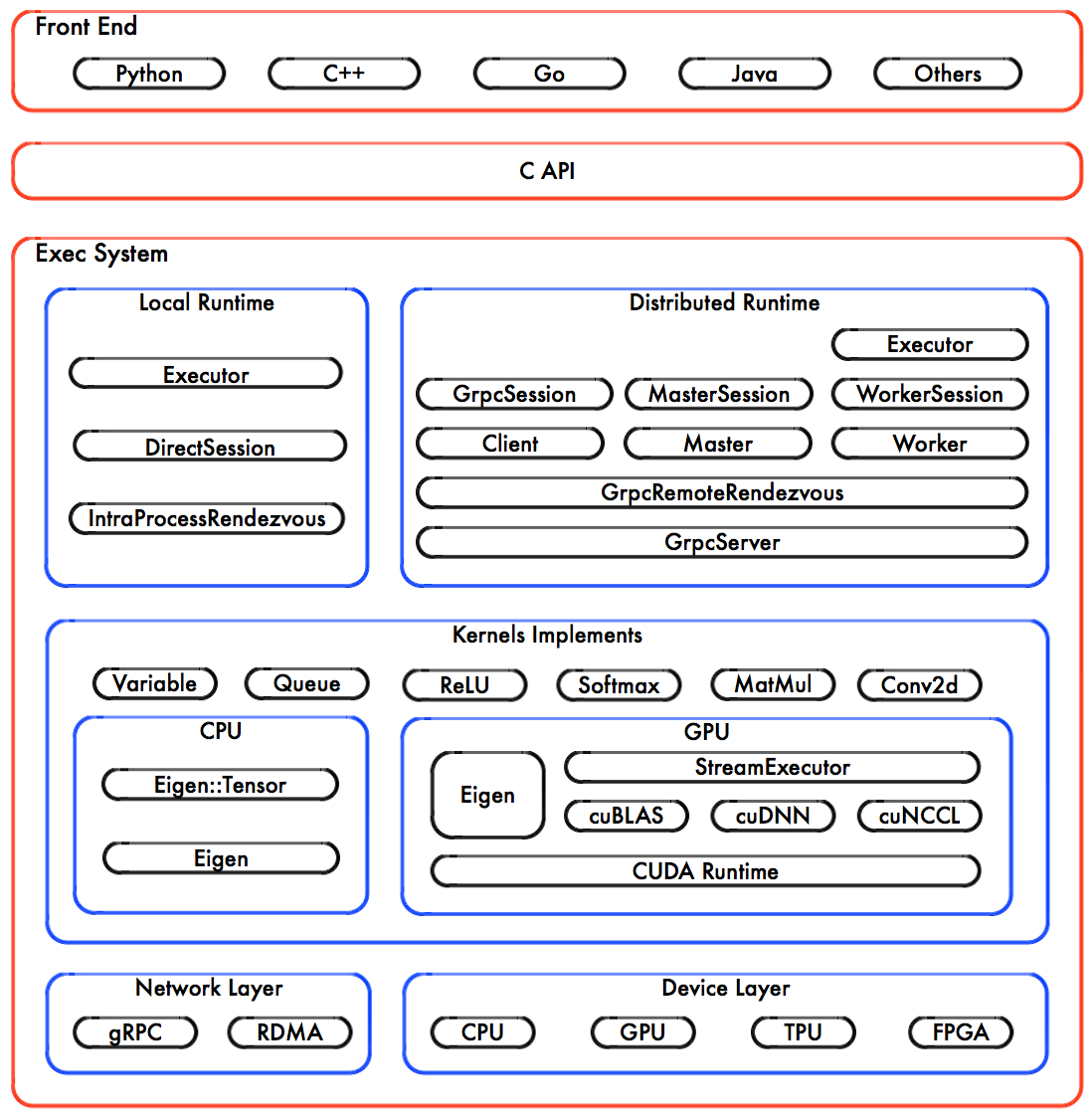
Tensorflow kernal launch 的过程
分析session执行的过程, 并分析Antman对执行过程的修改
函数调用链 Run()–>RunInternel()–>RunAsync()–>ScheduleReady()–>Process()
修改了direct_session.cc , 在session执行前后运行中间件框架
修改了executor.cc , 新增一个异步调用队列, 并将需要插入时间槽的异步Op加入队列,在OpManager线程中等待执行。
Session的执行
Session的代码逻辑在TensorFlow-with-dynamic-scaling/tensorflow/core/common_runtime/direct_session.cc的Run()函数中,
DirectSession::Run
Status DirectSession::Run(const RunOptions& run_options,
const NamedTensorList& inputs,
const std::vector<string>& output_names,
const std::vector<string>& target_nodes,
std::vector<Tensor>* outputs,
RunMetadata* run_metadata) {
//判断计算图是否构建
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(CheckNotClosed());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(CheckGraphCreated("Run()"));
//计数器
direct_session_runs->GetCell()->IncrementBy(1);
// Extract the inputs names for this run of the session.
//提取输入的张量名字和张量大小
std::vector<string> input_tensor_names;
input_tensor_names.reserve(inputs.size());
size_t input_size = 0;
for (const auto& it : inputs) {
input_tensor_names.push_back(it.first);
input_size += it.second.AllocatedBytes();
}
metrics::RecordGraphInputTensors(input_size);
// Check if we already have an executor for these arguments.
// 检查是否已经创建执行器, 没有的话, 创建
// 一般情况下 每个设备都有一个执行器, 负责这个设备上计算子图的执行
ExecutorsAndKeys* executors_and_keys;
RunStateArgs run_state_args(run_options.debug_options());
run_state_args.collective_graph_key =
run_options.experimental().collective_graph_key();
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(GetOrCreateExecutors(input_tensor_names, output_names,
target_nodes, &executors_and_keys,
&run_state_args));
{
mutex_lock l(collective_graph_key_lock_);
collective_graph_key_ = executors_and_keys->collective_graph_key;
}
// Configure a call frame for the step, which we use to feed and
// fetch values to and from the executors.
//设置函数调用帧的参数, Tensorflow使用feed和fetch字典来和执行器进行数据交互
//feed是输入, fetch是输出
//构建FunctionCallFrame call_frame, Session与执行器之间相互交互
//处理执行器的输入与输出
FunctionCallFrame call_frame(executors_and_keys->input_types,
executors_and_keys->output_types);
gtl::InlinedVector<Tensor, 4> feed_args(inputs.size());
for (const auto& it : inputs) {
if (it.second.dtype() == DT_RESOURCE) {
Tensor tensor_from_handle;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
ResourceHandleToInputTensor(it.second, &tensor_from_handle));
feed_args[executors_and_keys->input_name_to_index[it.first]] =
tensor_from_handle;
} else {
feed_args[executors_and_keys->input_name_to_index[it.first]] = it.second;
}
}
// 设置输入参数
const Status s = call_frame.SetArgs(feed_args);
if (errors::IsInternal(s)) {
return errors::InvalidArgument(s.error_message());
} else if (!s.ok()) {
return s;
}
const int64 step_id = step_id_counter_.fetch_add(1);
if (LogMemory::IsEnabled()) {
LogMemory::RecordStep(step_id, run_state_args.handle);
}
//准备好执行环境之后, 开始调用RunInternal执行计算
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(RunInternal(step_id, run_options, &call_frame,
executors_and_keys, run_metadata,
thread::ThreadPoolOptions()));
... ...
// 获取并处理计算图的执行结果
}
DirectSession::RunInternal()
// RunInternal会启动多个并行的执行器,
// 创建执行器的barrier, 确保执行器都执行完, 执行完后返回Run()函数
Status DirectSession::RunInternal(
int64 step_id, const RunOptions& run_options,
CallFrameInterface* call_frame, ExecutorsAndKeys* executors_and_keys,
RunMetadata* run_metadata,
const thread::ThreadPoolOptions& threadpool_options) {
const uint64 start_time_usecs = options_.env->NowMicros();
const int64 executor_step_count = executors_and_keys->step_count.fetch_add(1);
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Running all pre session run action in grouping //
// 在session计算执行之前添加SessionRunActionRegistry //
// 以运行在session开始之前的中间件 //
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SessionRunActionOptions action_options;
action_options.device_mgr = &device_mgr_;
action_options.sess_ptr = this;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(SessionRunActionRegistry::Global()->RunGrouping(
SessionRunActionRegistry::PRE_SESSION_RUN, action_options));
//
//
//标记运行状态
RunState run_state(step_id, &devices_);
... ... // profiler TraceMe
//构建 IntraProcessRendezvous 用于本地Tensor管理
run_state.rendez = new IntraProcessRendezvous(device_mgr_.get());
... ... // ifndef _ANDROID
// Start parallel Executors.
//开始并行执行器
//构建 ExecutorBarrier 用于协调多个 Executor 并行计算,保持 graph 一致性
const size_t num_executors = executors_and_keys->items.size();
ExecutorBarrier* barrier = new ExecutorBarrier(
num_executors, run_state.rendez, [&run_state](const Status& ret) {
{
mutex_lock l(run_state.mu_);
run_state.status.Update(ret);
}
run_state.executors_done.Notify();
});
... ... //构建args
// Register this step with session's cancellation manager, so that
// `Session::Close()` will cancel the step.
... ...//处理`Session::Close()`
// Use std::unique_ptr to ensure garbage collection
//创建线程池实际运行执行器
std::unique_ptr<thread::ThreadPool> threadpool_wrapper;
thread::ThreadPool* pool = nullptr;
...//设置线程池
//异步启动执行器
for (const auto& item : executors_and_keys->items) {
thread::ThreadPool* device_thread_pool =
item.device->tensorflow_device_thread_pool();
if (!device_thread_pool) {
args.runner = default_runner;
} else {
args.runner = [this, device_thread_pool](Executor::Args::Closure c) {
device_thread_pool->Schedule(std::move(c));
};
}
if (handler != nullptr) {
args.user_intra_op_threadpool = handler->AsIntraThreadPoolInterface();
}
/////////////// 执行器的启动///////////////////
item.executor->RunAsync(args, barrier->Get());
/////////////////////////////////////////////
}
//等待执行结果
WaitForNotification(&run_state, &step_cancellation_manager,
run_options.timeout_in_ms() > 0
? run_options.timeout_in_ms()
: operation_timeout_in_ms_);
... ...
//保存运行结果
if (!run_state.tensor_store.empty()) {
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(run_state.tensor_store.SaveTensors(
{executors_and_keys->callable_options.fetch().begin(),
executors_and_keys->callable_options.fetch().end()},
&session_state_));
}
... ...
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Running all post session run action in grouping //
// 在session计算执行结束之后添加SessionRunActionRegistry, //
// 以运行在session结束之后的中间件 //
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
uint64 session_end_time = tensorflow::Env::Default()->NowMicros();
action_options.sess_duration_us = time_duration_usecs;
action_options.graph_id = reinterpret_cast<uint64>(executors_and_keys);
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(SessionRunActionRegistry::Global()->RunGrouping(
SessionRunActionRegistry::POST_SESSION_RUN, action_options));
return Status::OK();
}
执行器逻辑
ExecutorState::RunAsyn()
# ExecutorState::RunAsync 的实现
# 概述:初始化ready队列, 开启线程池
void ExecutorState::RunAsync(Executor::DoneCallback done) {
const Graph* graph = impl_->graph_.get();
TaggedNodeSeq ready;
// 获取 context map,即运行时上下文
Device* device = impl_->params_.device;
const Status fill_status =
device->FillContextMap(graph, &device_context_map_);
if (!fill_status.ok()) {
done(fill_status);
return;
}
// 初始化 ready 队列,即存放入度为0的node
for (const Node* n : impl_->root_nodes_) {
DCHECK_EQ(n->in_edges().size(), 0);
ready.push_back(TaggedNode{n, root_frame_, 0, false});
}
if (ready.empty()) {
done(Status::OK());
} else {
num_outstanding_ops_ = ready.size();
root_frame_->iterations[0]->outstanding_ops = ready.size();
done_cb_ = std::move(done);
// 线程池入口
ScheduleReady(ready, nullptr);
}
}
ExecutorState::ScheduleReady()
# ExecutorState::ScheduleReady 的实现
# 概述:将节点分为 expensive & inexpensive 节点,将inexpensive节点放入 inline_ready 中
void ExecutorState::ScheduleReady(const TaggedNodeSeq& ready,
TaggedNodeReadyQueue* inline_ready) {
if (ready.empty()) return;
int64 scheduled_usec = 0;
if (stats_collector_) {
scheduled_usec = nodestats::NowInUsec();
}
if (inline_ready == nullptr) {
// 运行所有 ready ops
// 运行ready队列里的节点 ready是当前线程要处理的队列
for (auto& tagged_node : ready) {
runner_([=]() { Process(tagged_node, scheduled_usec); });
}
return;
}
// 将节点分类,运行 expensive node
const GraphView& gview = impl_->gview_;
const TaggedNode* curr_expensive_node = nullptr;
for (auto& tagged_node : ready) {
const NodeItem& item = *gview.node(tagged_node.node->id());
if (tagged_node.is_dead || !item.kernel_is_expensive) {
//
inline_ready->push_back(tagged_node);
} else {
//对于高开销节点启动新的线程去执行
if (curr_expensive_node) {
runner_(std::bind(&ExecutorState::Process, this, *curr_expensive_node,
scheduled_usec));
}
curr_expensive_node = &tagged_node;
}
}
if (curr_expensive_node) {
//高开销节点
if (inline_ready->empty()) {
// inline_ready为空, 将首个高开销节点放入inline_ready
inline_ready->push_back(*curr_expensive_node);
} else {
// inline_ready不为空, 将高开销节点放入其他线程中执行
runner_(std::bind(&ExecutorState::Process, this, *curr_expensive_node,
scheduled_usec));
}
}
... ...
}
ExecutorState::Process()
# ExecutorState::Process 详解
# 概述:线程池中跑的内容,代码太长不贴了。
# 主要流程:
# + 将当前节点添加到 inline_ready 队列中。
# + 循环从 inline_ready 队列获取节点并运行,运行完毕后执行 NodeDone(有可能会添加新节点到inline_ready队列)
# + 当inline ready队列为空时,跳出循环。
# 其他重要内容:
# + 运行节点通过 device 的 ComputeAsync 或 Compute 方法
# + 处理输出结果使用 ProcessOutputs 函数和 PropagateOutputs 函数
# + 计算结束后通过 NodeDone 来收尾
void ExecutorState::Process(TaggedNode tagged_node, int64 scheduled_nsec) {
WithContext wc(context_);
... ...
// Parameters passed to OpKernel::Compute.
TensorValueVec inputs;
DeviceContextVec input_device_contexts;
AllocatorAttributeVec input_alloc_attrs;
OpKernelContext::Params params;
params.step_id = step_id_;
// Override device's threadpool if user provides an intra_op_threadpool
Device* device = impl_->params_.device;
... ...
bool completed = false;
inline_ready.push_back(tagged_node);
uint64 sess_op_num = 0;
//循环处理inline_ready中的每个节点 直到为空
while (!IsAsyncGPUOpQueueEmpty() || !inline_ready.empty()) {
tagged_node = inline_ready.front();
inline_ready.pop_front();
... ...
//准备输入数据, 确保输入是有效的
s = PrepareInputs(item, first_input, &inputs, &input_device_contexts,
&input_alloc_attrs, &is_input_dead);
... ...
// 绝大多数的Op是同步计算模式, send/recv是异步计算模式
if (item.kernel_is_async) {
//异步计算, send/recv是高开销的
launched_asynchronously = true;
Device* kernel_device = impl_->params_.device;
// Only enqueue this op if it is an async GPU op.
if (need_to_insert_idle_time_ && (kernel_device->name()).find("GPU") != string::npos) {
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 把这个GPU Op放入async_gpu_op_queue队列中 如果需要在它启动之前插入时间槽的话
// Enqueue this GPU op therefore we can insert a time slot before launching this op.
// 将原本执行异步计算代码的Op放入自定义的async_gpu_op_queue队列中,
// 交由OpManager执行
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
sess_op_num++;
... ...
// Enqueue this asyn GPU op.
async_gpu_op_queue_lock_.lock();
async_gpu_op_queue.emplace_back(async_gpu_kernel);
num_queued_op.fetch_add(1);
async_gpu_op_queue_lock_.unlock();
} else {
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 不需要插入时间槽, 所以不放入async_gpu_op_queue队列
// Do not enqueue this op.
// 调用原本的计算异步的函数
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
device->ComputeAsync(async, &state->ctx, done);
} else {
// 同步计算
// Synchronous computes.
OpKernelContext ctx(¶ms, item.num_outputs);
nodestats::SetOpStart(stats);
... ... //进行计算 deivce->Compute(op_kernel, &ctx)
nodestats::SetOpEnd(stats);
//处理输出
s = ProcessOutputs(item, &ctx, &outputs, stats);
... ...
//传播输出
if (s.ok()) {
PropagateOutputs(tagged_node, &item, &outputs, &ready);
}
... ... //传播后处理
//结束
completed = NodeDone(s, item.node, ready, stats, &inline_ready);
}
} // while !inline_ready.empty()
if (sess_op_num > 0) {
// Record the total number of the queued op running in this session.
GPUResourceManagement* rm = GetGPUResourceManagement();
if (rm != nullptr) {
rm->SetExecutorQueuedOpNum(impl_, sess_op_num);
}
}
// This thread of computation is done if completed = true.
if (completed) ScheduleFinish();
}
ExecutorState::AsyncGPUOpManager()
void ExecutorState::AsyncGPUOpManager() {
uint64 sleep_time_us = 0;
need_to_insert_idle_time_ = false;
GPUResourceManagement* rm = GetGPUResourceManagement();
if (rm == nullptr) {
return;
}
while (!terminate_op_magager_thread_) {
//设置队列中的Op是否需要插入时间槽
need_to_insert_idle_time_ = rm->GetEstimatedIdleTime() > 0 ? true : false;
std::function<void(void)> queued_call_func = nullptr;
async_gpu_op_queue_lock_.lock();
if (!async_gpu_op_queue.empty()) {
queued_call_func = async_gpu_op_queue.front();
}
async_gpu_op_queue_lock_.unlock();
if (queued_call_func != nullptr) {
queued_call_func();
async_gpu_op_queue_lock_.lock();
if (!async_gpu_op_queue.empty()) {
async_gpu_op_queue.erase(async_gpu_op_queue.begin());
num_queued_op.fetch_sub(1);
}
async_gpu_op_queue_lock_.unlock();
// Estimate idle time
uint64 idle_time = rm->GetEstimatedIdleTime();
uint64 queued_op_num = rm->GetExecutorQueuedOpNum(impl_);
idle_time = queued_op_num > 0 ? (idle_time / queued_op_num) : 0;
usleep(idle_time);
uint64 remain_time = rm->GetEstimatedIdleTime();
remain_time = remain_time > idle_time ? (remain_time - idle_time) : 0;
rm->SetEstimatedIdleTime(remain_time);
}
usleep(default_check_interval);
}
return;
}
Antman对内存分配器的修改
主要新增了自己的vmen内存分配器, 调用host的内存
在TensorFlow-with-dynamic-scaling/tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_process_state.cc#做了修改
Allocator* GPUProcessState::GetGPUAllocator(const GPUOptions& options,
TfGpuId tf_gpu_id,
size_t total_bytes) {
CHECK(process_state_);
#if (defined(GOOGLE_CUDA) && GOOGLE_CUDA) || \
(defined(TENSORFLOW_USE_ROCM) && TENSORFLOW_USE_ROCM)
const string& allocator_type = options.allocator_type();
mutex_lock lock(mu_);
GpuIdUtil::CheckValidTfGpuId(tf_gpu_id);
if (tf_gpu_id.value() >= static_cast<int64>(gpu_allocators_.size())) {
gpu_allocators_.resize(tf_gpu_id.value() + 1);
}
AllocatorParts& allocator_parts = gpu_allocators_[tf_gpu_id.value()];
if (allocator_parts.allocator == nullptr) {
// Validate allocator types.
if (!allocator_type.empty() && allocator_type != "BFC") {
LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid allocator type: " << allocator_type;
return nullptr;
}
PlatformGpuId platform_gpu_id;
TF_CHECK_OK(GpuIdManager::TfToPlatformGpuId(tf_gpu_id, &platform_gpu_id));
int bus_id = BusIdForGPU(tf_gpu_id);
DCHECK_GE(bus_id, 0);
while (bus_id >= gpu_visitors_.size()) {
gpu_visitors_.push_back({});
}
se::StreamExecutor* stream_exec =
GpuIdUtil::ExecutorForPlatformGpuId(platform_gpu_id).ValueOrDie();
GPUMemAllocator* sub_allocator = new GPUMemAllocator(
stream_exec,
platform_gpu_id,
(options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction() > 1.0 ||
options.experimental().use_unified_memory()),
gpu_visitors_[bus_id], {});
GPUBFCAllocator* gpu_bfc_allocator =
new GPUBFCAllocator(sub_allocator, total_bytes, options,
strings::StrCat("GPU_", tf_gpu_id.value(), "_bfc"));
Allocator* gpu_allocator = gpu_bfc_allocator;
// GPUVMemAllocator will allocate host memory as backup after running out of
// gpu device memory to avoid OOM failures
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
gpu_allocator = maybe_create_gpu_vmem_allocator(gpu_allocator,
bus_id,
platform_gpu_id,
tf_gpu_id.value(),
stream_exec);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SharedCounter* timing_counter = nullptr;
if (options.experimental().timestamped_allocator()) {
timing_counter = new SharedCounter;
gpu_bfc_allocator->SetTimingCounter(timing_counter);
}
// If true, checks for memory overwrites by writing
// distinctive patterns on both ends of allocated memory.
if (useCudaMemoryGuardAllocator()) {
gpu_allocator = new GPUDebugAllocator(gpu_allocator, platform_gpu_id);
gpu_allocator = new GPUNanResetAllocator(gpu_allocator, platform_gpu_id);
} else if (useCudaMallocAllocator()) {
// If true, passes all allocation requests through to cudaMalloc
// useful for doing memory debugging with tools like cuda-memcheck
// **WARNING** probably will not work in a multi-gpu scenario
gpu_allocator =
new GPUcudaMallocAllocator(gpu_allocator, platform_gpu_id);
}
Allocator* recording_allocator = nullptr;
if (process_state_->ProcessState::FLAGS_brain_gpu_record_mem_types) {
ProcessState::MemDesc md;
md.loc = ProcessState::MemDesc::GPU;
md.dev_index = platform_gpu_id.value();
md.gpu_registered = false;
md.nic_registered = true;
recording_allocator = new internal::RecordingAllocator(
&process_state_->mem_desc_map_, gpu_allocator, md, &mu_);
}
allocator_parts = {std::unique_ptr<Allocator>(gpu_allocator),
std::unique_ptr<SharedCounter>(timing_counter),
gpu_bfc_allocator, sub_allocator,
std::unique_ptr<Allocator>(recording_allocator)};
}
if (process_state_->ProcessState::FLAGS_brain_gpu_record_mem_types) {
return allocator_parts.recording_allocator.get();
} else {
return allocator_parts.allocator.get();
}
#else
LOG(FATAL) << "GPUAllocator unavailable. Not compiled with --config=cuda or "
"--config=rocm.";
return nullptr;
#endif // GOOGLE_CUDA || TENSORFLOW_USE_ROCM
}
gpu_process_state 是个单例模式, 只有一个实例存在
/*static*/ GPUProcessState* GPUProcessState::singleton(GPUProcessState* ps) {
static GPUProcessState* instance = ps ? ps : new GPUProcessState;
DCHECK((!ps) || (ps == instance))
<< "Multiple calls to GPUProcessState with non-null ps";
return instance;
}
GPUProcessState::GPUProcessState() : gpu_device_enabled_(false) {
process_state_ = ProcessState::singleton();
}